To say coronavirus pandemic has caused mayhem throughout the world in the last couple of months would be an understatement. As of writing this post, the official reported infected cases is more than 156k+, with close to 5.8k+ deaths and 75k+ recoveries across the planet. As a technologist, I wanted to take a look at a few things which were floating about in the news media regarding the killing of the virus and a potential disinfection. I am in no means an expert in this domain, but I will try to base my thoughts on actual scientific research done on the topic. This post is meant to be informative and is by no means exhaustive. If you find any discrepancy in post feel free to comment below with valid points and I will be happy to correct my content.
Primer
Coronavirus pandemic is an infectious disease outbreak. World Health Organisation(WHO) renamed the disease to COVID-19[1] which is an abbreviation for COrona VIrus Disease – 2019 (Its 2019 and NOT 2020 because the first reported case in China was in 2019). The causative virus for the disease is SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome CoronaVirus 2). If the name seems similar, it’s a close relative of the virus(SARS-CoV) which caused the SARS outbreak in 2003 in Asia. Interesting Article on the naming convention if you want to read more from Nature Journal[2].
CDC says that COVID-19 spreads via person to person interaction if they are in close contact with one another or through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person sneezes/coughs which can be inhaled by a non-infected person. There is also the possibility that a person can get infected if they touch a surface or an object with the virus and then touching their mouth, nose or eyes. Hence the precautionary measure to always wash your hands with soap and water when you are coming in from outside and the minimize touching your face with your hands as much as possible. Basic reproduction number of SARS-CoV-2 is between 1.4–3.8[3], that means each infection from the virus will result in 1.4 – 3.8 new infections if it’s not controlled properly.
A new study[4] published on March first week (It’s in preprint so not officially peer-reviewed yet) investigated the stability of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 on physical surfaces. Results do show that viruses are similar and it could be detected up to 24 hours on cardboard, 2-3 days on plastic and steel. This is slightly troubling information as it can potentially grow into a source of spreading of the virus.
Hence the sudden spike in interest in disinfection of surfaces. I have seen a few news media posts hailing solutions like ozone cleaning as the thing that will save the human race from this virus[5]. I wanted to see what science has to say about this and following is the compilation based on what I could find with some scientific research backing. I am linking only research papers and studies which are openly available to access for the general public. I am focussing on possible technologies which can help in disinfecting surfaces and potentially rooms. (I am not including basic chemical reagent disinfection category in this post. Please check European CDC protocol guidelines linked towards the end)
Two possible ways I could classify disinfection by the use of technology was
1. Ozone cleaning
2. UV Light cleaning
Ozone Cleaning:
Let’s talk about the science first. Ozone (03) is a highly reactive oxidant and contains 3 oxygen atoms. Ozone is created when a high energy particle splits Oxygen molecule into its 2 atoms. These atoms recombine with another stable 02 molecule to form Ozone. This same Ozone can act as a shield against harmful UV rays from the sun. The UV rays get used up by the ozone layer in the atmosphere.
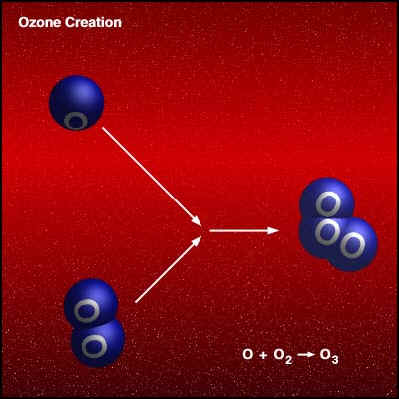
Picture Courtesy: http://www.theozonehole.com
Ozone is highly reactive. It has a half-life period (Amount of time taken to half its concentration) of close to 40mins at good air circulation and humidity concentrations[6]. It will oxidise most metals in an effort to reach its stable oxygen state. Ozone cleaning is a method of disinfection as the reactive ozone is highly efficient in killing pathogens it comes in contact with. There has been quite a lot of studies which prove that pathogens like bacteria and viruses can be killed with a high enough ozone concentration in the air[7][8]. There has been enough evidence of using ozone to kill the SARS-CoV virus after the SARS outbreak in 2003. Although I couldn’t find a single published study on SARS-CoV-2 and its inactivation by ozone, I think we can say with a good deal of certainty that it can kill SARS-CoV-2 as its structure is closely related to SARS-CoV.
Ozone Production:
Ozone can be produced in several ways. One of the most common methods is via the corona discharge technique. It’s the electrical discharge which happens in a medium surrounding a charged conductor. It is usually produced by increasing the voltage of a conductor to make the nearby electric field to be very high such that it starts imparting high energy particles to its surrounding medium. You can see this effect as a bluish tinge next to high voltage conductors. This ionises the atmospheric oxygen to potentially form ozone. In certain systems, you flow a stream of oxygen to the charged plate to increase the ozone concentrations.
In my previous blog post, we saw how to create a $10 Air Ioniser. Do check it out if you want to learn how it works. A side effect of that system is the potential formation of ozone. We can increase the output voltage of that system by increasing the number of voltage multiplier stages(but losses start adding up beyond a point) or better by increasing the input power supply from 220V AC to a larger voltage like 500-600V AC with a step-up transformer. If the output voltage is high enough, you will be able to distinctly see corona discharge happening as a bluish tinge at the end of the sharp conductors at the end. So this system can potentially be used to create ozone as well.
Other ways of creating ozone are more or less via similar principles like cold plasma technique. Cold Plasma ozone generation is done when ionisation is created between a dielectric barrier and oxygen is passed next to it. Due to the dielectric barrier, the corona is created over a larger area. The high energy causes the oxygen to get converted to ozone.
Another way is the nature’s way of creating ozone. Ultraviolet rays from the sun hit oxygen and create ozone. We utilise this same principle to create ozone. We will go over this in the UV section
UV Light Cleaning
Ultraviolet rays are invisible to the human eye and it lies beyond the blue region in the electromagnetic spectrum. UV spectrum spans the range of 100nm to 400nm in wavelength and is subclassified into UV A, UV B, UV C.
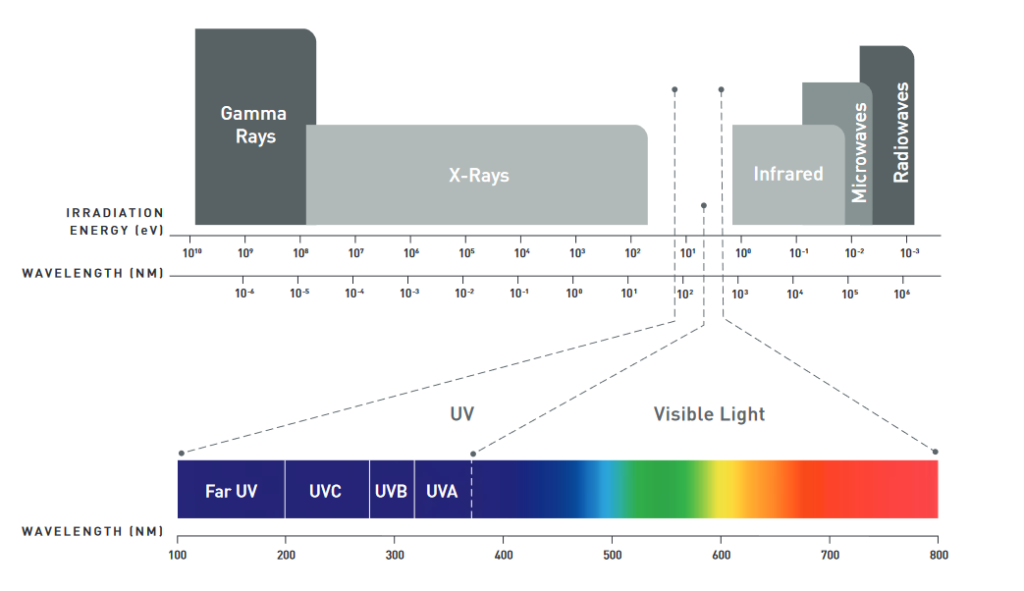
Electromagnetic Spectrum Picture Courtesy Klaran[9]
UV A — (315nm – 400nm) – Most Harmful Range. Can penetrate deep into the skin and causes tanning. Can potentially cause skin cancer.
UV B — (280nm – 360nm) – Reaches the outer skin layer and used in phototherapy[10]
UV C — (200nm – 280nm) – Germicidal range is from 250nm – 280nm
In the Far UV range, Around 185nm can be in the ozone production range, here UV light helps in the creation of ozone.
In the pure UV germicidal case, we are interested in the UV C range. It has been proven that Germicidal UV light can deactivate the DNA of bacteria and viruses. It penetrates the cells of the pathogens and damages the nucleic acid and renders them unable to reproduce.
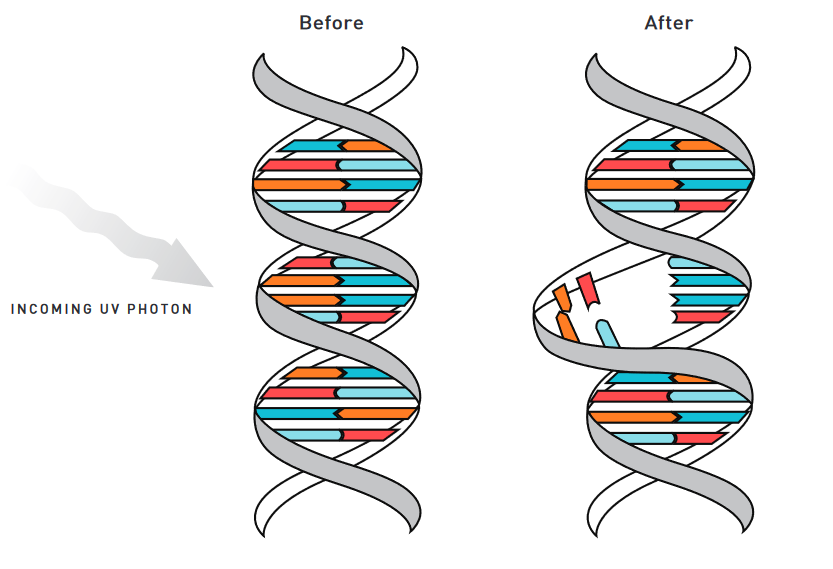
UVC LEDs and UV lamps are now relatively common in the market. Their disinfection rate(UV dose) is a function of UV intensity and exposure time. That means a higher intensity or a longer exposure time will make sure that the chances of killing pathogens are higher. I highly recommend reading the white paper from Klaran which lists the UV dose needed to kill different kinds of pathogens like viruses and bacteria[11]. Again I couldn’t find a study linked directly with the UV and SARS-CoV-2. Theoretically, it should work.
UV lamps also help in speeding up the killing process with the generation of ozone. UV rays can ionise the oxygen to become ozone. Ozone generated will help in the faster killing of the pathogens present in the air.
Usage scenarios:
Now that you understand the science behind it. Let’s try to see where these can be used in the case of COVID-19 outbreak, what are its harmful effects and whether these need to be used at all.
These solutions (at least in my opinion) makes sense to be used in a public cleansing drive setup. Assume that you need to disinfect a room which you know for a fact has been infected by a patient (Imagine hospital rooms and likewise). Then using either of these solutions for a good amount of time is pretty much guaranteed to give you a sterile environment. As I mentioned before, SARS-CoV-2 is more or less likely to be killed by either a UV disinfection or via ozone as its close cousin of SARS-CoV, in which this has been tested before, was successfully inactivated. But studies are currently on specifically testing on SARS-CoV-2.
The main disadvantage of both these techniques is the harm it can do. Both these are to be used in closed rooms only. A high concentration of ozone is very bad for your respiratory system. It can cause inflammation and irritation in your airways. It causes shortness of breath, coughing and can aggravate chronic lung conditions like asthma. [12, 13]. Using Ozone generators is a bad idea unless it’s in a controlled environment wherein there is no human in the room for the entire duration of the ozone generation and an additional 1-2 hours after that, just for the unstable ozone to reduce in concentration by itself. So an ozone generator with a timer would be an apt solution where its necessary.
Coming to the UV sterilisation technique, the same is applicable. Random UV light/lamps can cause serious skin, eye irritation, reddening and swelling. Long term exposure can lead to skin cancer[10]. Hence proper protective gear needs to be worn when handling UV lamps. UV lamps can be turned on in a closed room with a timer to ensure maximum irradiation. Care has to be taken such that there is no human presence while the UV lamp is ON.
Conclusion:
Is it worth it considering the associated health hazards? I would suggest using it in only controlled environments by people who know what they are doing. You may ask “Can I buy an ozone generator and leave it running in a room to disinfect it?” It is an OK thing to do if you take enough precautions making sure that you or your family doesn’t breathe in the ozone. Is it worth the risk? That’s a call you need to make.
I can foresee these being used in a public setting and not necessarily in a home use case for disinfection. You should also take look at US Environmental protection agency’s (EPA) list of Disinfectants for Use Against SARS-CoV-2[14] which include chemical reagents for wiping down surfaces. Also, do read up on European CDC guidelines for environmental cleaning in non-healthcare facilities exposed to SARS-CoV-2[15] which suggests the use of normal household materials for cleaning with decent results.
(If you plan on using any of these solutions, please doubly make sure you understand the risks and take precautionary measures as needed.)
To conclude, Stay calm. Stay safe. Avoid large gatherings. Wash your hands multiple times a day. Basic hygiene will go a long way in preventing the spread of the disease.
Fresh thinking